What is ERP?
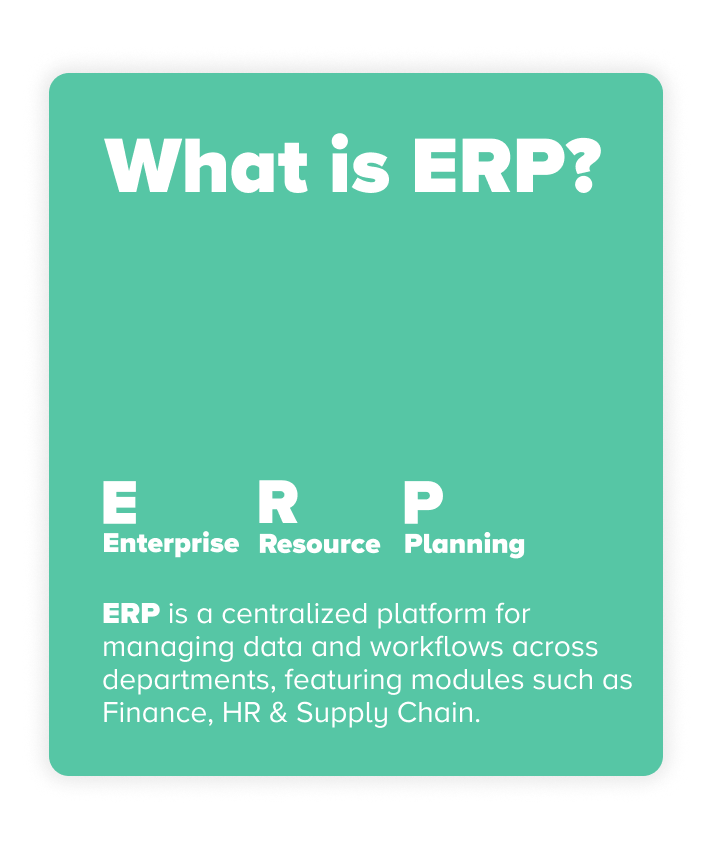
ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning. It is a software system that integrates all the core processes and functions of a business into a single, unified platform.
It serves as a centralized system for various departments, including accounting, procurement, project management, supply chain operations, and human resources. This ensures all teams can access consistent, up-to-date information, driving better communication and collaboration. At its core, ERP is about unifying business processes. Instead of working with separate tools in silos, ERP systems streamline operations by providing a single platform for managing workflows and reporting.
Common ERP modules
ERP systems are designed as modular platforms that support diverse business functions through a unified and integrated architecture. While the availability of specific modules varies by provider, ERP platforms commonly include the following core capabilities:
Finance & Accounting
A foundational module in nearly all ERP solutions, Finance & Accounting manages core financial operations, including accounts payable and receivable, general ledger, budgeting, tax compliance, and financial reporting. It provides organizations with accurate, real-time visibility into financial performance and supports regulatory compliance.
Human Resources (HR)
The HR module facilitates the full employee lifecycle—from recruitment and onboarding to payroll, time tracking, and performance management. It centralizes workforce data to enable strategic workforce planning and streamlined talent management.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
CRM functionality helps organizations manage customer interactions, sales pipelines, and marketing campaigns. By consolidating customer data, this module supports personalized engagement strategies and enhances service delivery.
Project management
This module supports planning, execution, and monitoring of projects. It tracks timelines, budgets, resources, and milestones to ensure delivery against objectives. Integrated collaboration tools help cross-functional teams stay aligned and agile.
Reporting & analytics
Data-driven decision-making is a cornerstone of modern ERP systems. Integrated reporting and analytics consolidate data across modules, delivering insights through dashboards, KPIs, and automated reports to support strategic and operational decisions.
Procurement & supply chain
These modules optimize the sourcing, purchasing, and logistics functions across the organization. They provide real-time visibility into inventory, supplier performance, and order fulfillment, improving operational efficiency and cost control.
Benefits of implementing an ERP system
Investing in ERP software can transform the way an organization operates. Below are the key benefits businesses experience when adopting ERP:
-
Improved efficiency and productivity: By automating repetitive tasks and reducing manual data entry, ERP systems free up valuable time for employees, allowing them to focus on more strategic tasks. This allows them to focus on higher-value activities that drive growth.
-
Enhanced data accuracy: ERP integrates data across departments into a single platform, ensuring that information is both consistent and accurate. This minimizes errors associated with manual inputs and siloed systems.
-
Better collaboration: With a unified system, departments can break down communication barriers. Teams can share information easily, ensuring smooth workflows and collaborative problem-solving.
-
Real-time insights: ERP systems provide companies with real-time data and analytics, enabling managers to make informed, timely business decisions.
-
Cost savings: Although implementing an ERP system requires an initial investment, it reduces long-term operational costs by improving resource allocation, inventory management, and budgeting.
-
Scalability: As businesses grow, ERP systems can scale with them. Modern ERPs are modular, meaning businesses can implement new features as needed without disrupting operations.
Industries that benefit from ERP
ERP systems are versatile and can be tailored to fit organizations across various industries. Some industries that frequently deploy ERP include:
The role of AI in ERP
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is redefining ERP systems, transforming them from transactional engines into intelligent platforms. While adoption and capabilities vary, AI is increasingly being embedded into ERP solutions to drive smarter, faster, and more predictive decision-making. Key applications include:
 Predictive analytics
Predictive analytics
AI algorithms analyze historical and real-time data to uncover trends and generate forecasts, enabling businesses to anticipate demand, mitigate risks, and optimize planning.
 Process automation
Process automation
AI enhances process efficiency by automating repetitive tasks such as invoice matching, approvals, and data entry. This reduces errors and frees up human capital for more value-added work.
 Conversational interfaces
Conversational interfaces
Natural Language Processing (NLP) enables intuitive interaction with ERP systems. Users can access information or complete tasks using everyday language, improving user adoption and system accessibility.
 Real-time decision support
Real-time decision support
AI-enhanced ERP systems provide real-time recommendations based on current data and context, whether reallocating resources, adjusting budgets, or identifying anomalies.
 Intelligent assistance
Intelligent assistance
Digital assistants and AI agents help users navigate complex workflows, offer proactive suggestions, and streamline common tasks. These tools enhance productivity and user experience across the organization.
Key considerations when choosing an ERP system
With so many ERP providers to choose from, selecting the right solution for your business can feel overwhelming. Here are the most important factors to evaluate:
-
Your business needs - Start by identifying the specific challenges you want the ERP system to address. Do you need it primarily for financial management or supply chain tracking? A clear understanding of your needs will guide your decision-making process.
-
Scalability - Choose a system that can grow with your company. A modular ERP solution allows you to add functionalities as your business expands.
-
Integration capabilities - Ensure the ERP system you select can integrate smoothly with existing tools, such as CRM software or industry-specific systems.
-
User-friendliness - A complex system with a steep learning curve can hinder productivity. Look for an intuitive interface that employees can easily adopt.
-
Cloud vs. on-premises - Modern ERP systems are often Cloud-based, offering flexibility by allowing employees to access the system from anywhere. For organizations with strict data control requirements, an on-premises solution might be preferable.
-
Support and training - Does the vendor offer onboarding support, training resources, and responsive customer service? This is critical to ensure a smooth implementation process.
-
Cost - Compare the pricing structures of different ERP vendors. Keep in mind the total cost of ownership, including implementation, licensing, and ongoing support fees.
Are you ready for ERP?
Not sure if your business could benefit from an ERP system? Here are some tell-tale signs:
 Data duplication
Data duplication
Your teams are frequently duplicating tasks or re-entering data.
 Disconnected systems
Disconnected systems
You rely on multiple software tools that don’t communicate with each other.
 Limited data visibility
Limited data visibility
Employees struggle to access critical business data in real-time.
 Inefficient processes
Inefficient processes
Your current workflows can’t keep up with business growth or increasing customer demands.
 Reporting challenges
Reporting challenges
Your financial reporting is time-consuming and prone to errors.
Empower your organization with ERP
ERP systems are an essential tool for businesses of all sizes. By adopting ERP, you are integrating your processes and also equipping your organization with the tools to remain competitive and agile in an unpredictable market.
ERP FAQs
How does an ERP system benefit an organization?
An ERP system integrates data from various business functions into a single source truth, making it easier to manage and analyze. This integration provides full transparency and visibility across people, finances, and projects, which enhances forecasting, reporting, and compliance.
How does Cloud ERP improve security?
Cloud ERP solutions are often hosted by major Cloud providers, like Microsoft Azure, who offer enhanced security measures and constant monitoring from their own internal security teams. These providers have extensive resources to ensure data security, often exceeding the capabilities of on-premises systems.
Why should I migrate from on-premises to Cloud-based ERP?
Organizations might migrate to Cloud-based ERP for several reasons, including integrated data, cost savings, improved maintenance, enhanced scalability, and the ability to leverage AI and automation for increased productivity.
What factors should be considered when choosing an ERP provider?
When choosing an ERP provider, consider the ease of implementation, the specific benefits and use of their products, customer testimonials, and the support provided during the onboarding process. Unit4, for example, emphasizes a people-first approach and offers a comprehensive suite of Cloud-based ERP solutions.
What role will AI and mobile technology play in the future of ERP?
The future of ERP systems lies in their ability to harness emerging technologies such as AI (Artificial Intelligence), machine learning, and IoT (Internet of Things). These advancements will make ERP systems even smarter, offering predictive analytics, enhanced automation, and deeper insights. Additionally, mobile ERP will be a game-changer. Employees will no longer be tied to desktops but can access their systems on the go, improving flexibility and productivity.

